
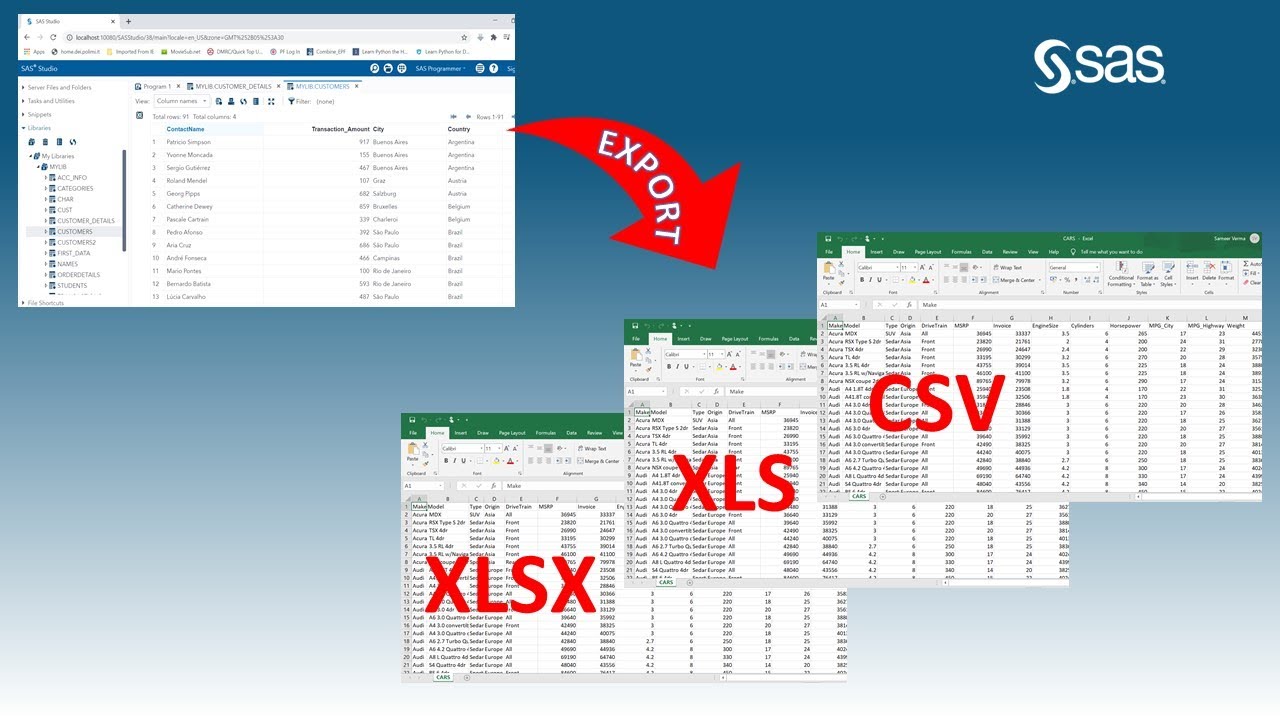
However, with the LIBNAME statement’s ENGINE option, you can also create libraries to import and export Excel files. Normally, you use the LIBNAME statement to create a library to store your SAS datasets. The SAS code below exports the work.my_data dataset to Excel and creates a file called cars.xlsx.Įxport data from SAS to Excel with the LIBNAME Statement The LIBNAME StatementĪ less known, but also very efficient way to export data from SAS to Excel is by creating a library with the LIBNAME statement. For example, if you export data to Excel, the SAS dataset cannot exceed the maximum of 1,048,576 rows and 16,384 columns. It depends on the file type how much data SAS can export. The DBMS=-option specifies the type of file the EXPORT procedure creates (e.g.
Keep in mind that the complete path (location and file name) can’t exceed 201 characters. The OUTFILE=-option specifies the location and file name of the exported dataset. When you export a dataset to Excel, you can use dataset options such as KEEP, RENAME, and WHERE in the DATA=-option. You can either use a one- or two-level SAS name (i.e., with or without libref). The DATA=-option specifies the SAS dataset you want to export.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
